Graph Approaches for Software Engineeering: Difference between revisions
| Line 220: | Line 220: | ||
== ⌘⌘ Ideas for SimpleGraph future Progress == | == ⌘⌘ Ideas for SimpleGraph future Progress == | ||
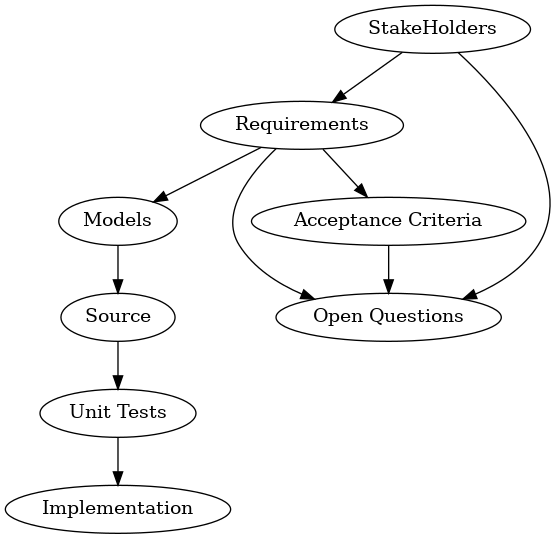
* more Software-Engineering related modules | <graphviz> | ||
* more Visualization options | digraph Objects9000 { | ||
* Visualized Editor e.g. with [https://developers.google.com/blockly/ blockly] | RQ [ label="Requirements" ] | ||
AC [ label="Acceptance Criteria" ] | |||
OQ [ label="Open Questions" ] | |||
SH [ label="StakeHolders" ] | |||
Test [ label="Unit Tests" ] | |||
Model [ label="Models" ] | |||
Impl [ label="Implementation" ] | |||
SH -> RQ | |||
RQ -> Model -> Source -> Test -> Impl | |||
RQ -> AC | |||
RQ -> OQ | |||
SH -> OQ | |||
AC -> OQ | |||
} | |||
</graphviz> | |||
* more Software-Engineering related modules e.g. for Modelling,Requirements Engineering | |||
* more Visualization options e.g. like/with [http://prefuse.org/ prefuse] | |||
* Visualized Editor e.g. like/with [https://developers.google.com/blockly/ blockly] | |||
* better integration with other programming languages | * better integration with other programming languages | ||
Revision as of 09:40, 18 February 2019
<slideshow style="bitplan" headingmark="⌘⌘" incmark="…" scaled="true" font="Comic Sans MS, Calibri, cursive" >
- title
Graph Approaches for Software Engineering
- author
- Wolfgang Fahl Wolfgang Fahl info@bitplan.com
- footer
- Applying the OpenSource Project SimpleGraph and it's modules to Software Engineering
- subfooter
- sebis Oberseminar TUM
</slideshow>
⌘⌘ Wolfgang Fahl
| |
 Peugeot Ion |
 Giant Explore |
⌘⌘ The World as a Graph
If the world is represented as a Graph it would be nice to have a Simple Graph Navigation Language

see SMWCon Fall 2018
⌘⌘ Why I am here
⌘⌘ Prehistory
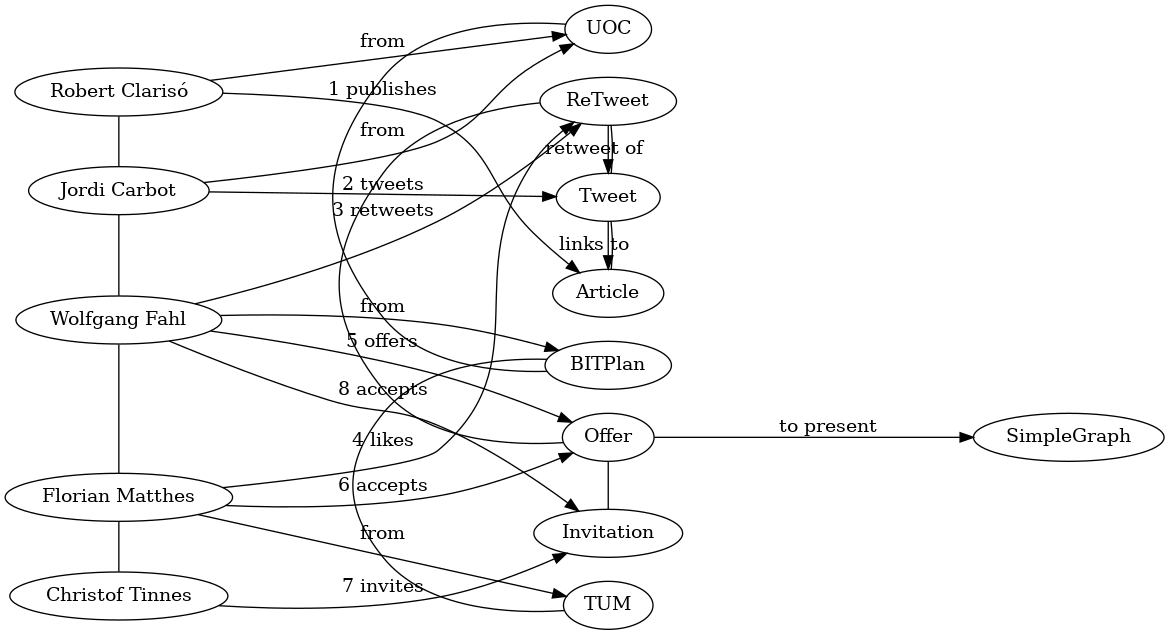
⌘⌘ Graph Kernels for Model Driven Software Engineering
5 Steps
- Decide how the model should be encoded into a graph
- Translate each of the models into a labeled graph
- Select the graph kernel algorithm to be used
- Load all the graphs and compute the graph kernel
- Exploit the information in the kernel matrix
⌘⌘ Use SimpleGraph for the 5 Steps
⌘⌘ Step 1: Decide how the model should be encoded into a graph
Each SimpleGraph Module transforms data from some API to a Graph representation. The transformation is usually as "straight-forward" or "natural" as possible.
⌘⌘ Step 2: Translate each of the models into a labeled graph
Each SimpleGraph Module uses the following steps to translate from an API to the graph
- connect()
- moveTo()
⌘⌘ Step 3: Select the graph kernel algorithm to be used
SimpleGraph is based on Apache Gremlin/Tinkerpop so all the algorithm and libraries around this graph environment are directly available. If a different graph kernel and or algorithm is needed than the graph can be translated / imported via standard graph import/export formats and or import/export adapters and utilities.
BITPlan e.g. often uses Semantic MediaWiki  as a suitable environment.
as a suitable environment.
⌘⌘ Step 4: Load all the graphs and compute the graph kernel
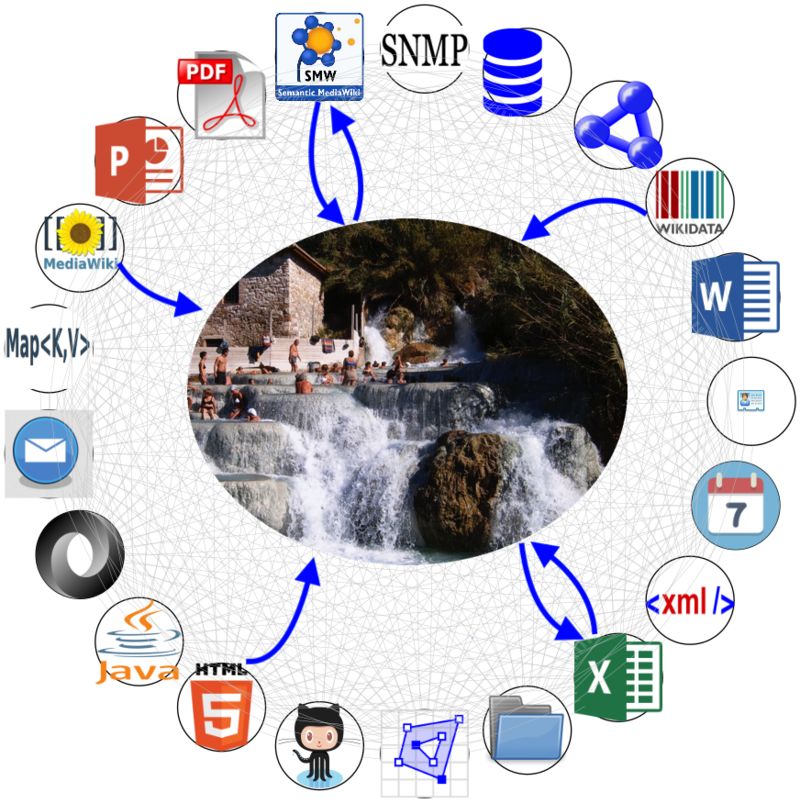
Simplegraph is based on the Hub&Spoke approach. Any combination of modules/API can be applied. Currently there are some 20 different modules to choose from.
⌘⌘ Step 5: Exploit the information in the kernel matrix
There are two modes for exploiting the information:
- OLAP - Online Analytical Processing / Graph Query
- OLTP - Online Transaction Processing / Graph Traversal
⌘⌘ What is SimpleGraph?
Simplegraph allows to work with "graphized" information source from a combination of APIs that are made available as modules.
|-
|style="text-align: center; width: 120px" |  FileSystem
|style="text-align: left" | FileSystem
|style="text-align: left" | java.io.File
|style="text-align: left" | makes your FileSystem accessible via the Java FileSystem API
|-|-
|style="text-align: center; width: 120px" |
FileSystem
|style="text-align: left" | FileSystem
|style="text-align: left" | java.io.File
|style="text-align: left" | makes your FileSystem accessible via the Java FileSystem API
|-|-
|style="text-align: center; width: 120px" |  GitHub
|style="text-align: left" | GitHub
|style="text-align: left" | GitHub GraphQL Api v4
|style="text-align: left" | makes GitHub content accessible to Graph processing.
|-|-
|style="text-align: center; width: 120px" |
GitHub
|style="text-align: left" | GitHub
|style="text-align: left" | GitHub GraphQL Api v4
|style="text-align: left" | makes GitHub content accessible to Graph processing.
|-|-
|style="text-align: center; width: 120px" |  Java
|style="text-align: left" | Java
|style="text-align: left" | javaparser
|style="text-align: left" | makes Java code parse results accessible to Graph processing.
|-|-
|style="text-align: center; width: 120px" |
Java
|style="text-align: left" | Java
|style="text-align: left" | javaparser
|style="text-align: left" | makes Java code parse results accessible to Graph processing.
|-|-
|style="text-align: center; width: 120px" | ![]() Mail
|style="text-align: left" | Mail
|style="text-align: left" | E-Mail access for rfc822 and MIME formatted Mailbox files (e.g. Thunderbird)
|style="text-align: left" | makes Mail data available via Apache Mime4J
|-|-
|style="text-align: center; width: 120px" |
Mail
|style="text-align: left" | Mail
|style="text-align: left" | E-Mail access for rfc822 and MIME formatted Mailbox files (e.g. Thunderbird)
|style="text-align: left" | makes Mail data available via Apache Mime4J
|-|-
|style="text-align: center; width: 120px" |  SMW
|style="text-align: left" | SMW
|style="text-align: left" | SemanticMedia Wiki API
|style="text-align: left" | makes Semantic MediaWiki accessible via the SMW API
|-|-
|style="text-align: center; width: 120px" |
SMW
|style="text-align: left" | SMW
|style="text-align: left" | SemanticMedia Wiki API
|style="text-align: left" | makes Semantic MediaWiki accessible via the SMW API
|-|-
|style="text-align: center; width: 120px" | ![]() XML
|style="text-align: left" | XML
|style="text-align: left" | org.w3c.dom
|style="text-align: left" | makes XML dom parse results accessible to Graph processing.
|-
XML
|style="text-align: left" | XML
|style="text-align: left" | org.w3c.dom
|style="text-align: left" | makes XML dom parse results accessible to Graph processing.
|-
⌘⌘ What is Apache TinkerPop/Gremlin?
 Apache Tinkerpop is an Open Source project. Gremlin is the GraphTraversal Language for it.
Apache Tinkerpop is an Open Source project. Gremlin is the GraphTraversal Language for it.
- OLTP - Online Transaction Processing - Navigation and Processing
- OLAP - Online Analytical Processing - Queries
- - Example - Ancestors of King James
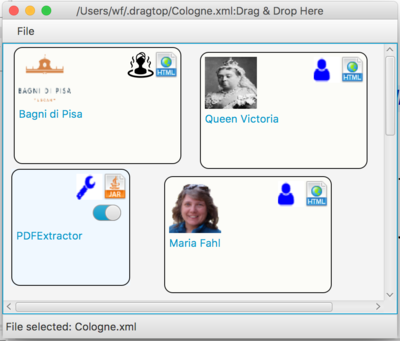
⌘⌘ SimpleGraph Dragtop
The Dragtop Open Source Software makes the SimpleGraph modules available for direct access from your Desktop. By simple drag and drop of the input onto the dragtop and then dropping a "tool" onto the dragtop you can combine the module functionality as you see fit.
⌘⌘ Example: The 5 Steps in SimpleGraph
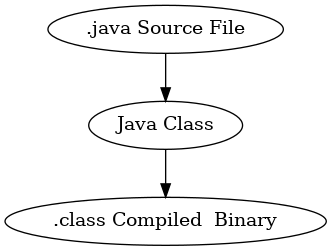
⌘⌘ Step 1: Decide how the model should be encoded into a graph
- .java Source Files: FileSystem module
- Java Classes: JavaSystem
- .class Files: Filesystem module (Bytecode parser?)
⌘⌘ Step 2: Translate each of the models into a labeled graph
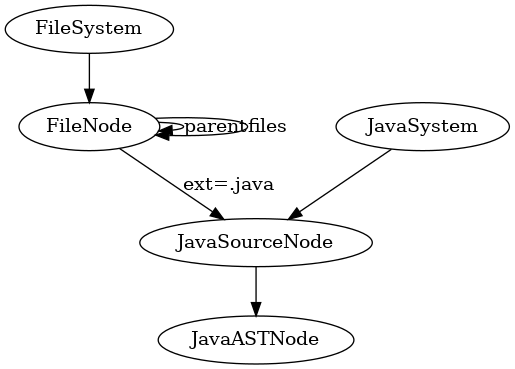
⌘⌘ Step 3: Select the graph kernel algorithm to be used
FileSystem fs=new FileSystem();
FileNode start = (FileNode) fs.connect("").moveTo(aroot.getPath());
start.recursiveOut("files",Integer.MAX_VALUE);
List<Vertex> javaFileNodes=start.g().V().has("ext", "java").toList();
List<Vertex> classFileNodes=start.g().V().has("ext", "class").toList()
⌘⌘ Step 4: Load all the graphs and compute the graph kernel
<HTML5video width="960" height="600" controls autoplay="false" loop="false">JavaAnalyzerDragAndDrop2019-02-18</HTML5video>
⌘⌘ Step 5: Exploit the information in the kernel matrix
- Visualize
- Store
- Mix and match with other sources
⌘⌘ How to benefit and participate
- Stay in touch with Wolfgang Fahl
- Ask StackOverFlow questions on SimpleGraph
- Participate in the GitHub SimpleGraph Open Source Project
- Join the SimpleGraph Mailinglist
- Collaborate on Projects with BITPlan
- Write papers related to SimpleGraph
⌘⌘ Ideas for SimpleGraph future Progress
- more Software-Engineering related modules e.g. for Modelling,Requirements Engineering
- more Visualization options e.g. like/with prefuse
- Visualized Editor e.g. like/with blockly
- better integration with other programming languages