Difference between revisions of "Gremlin Basics"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
} | } | ||
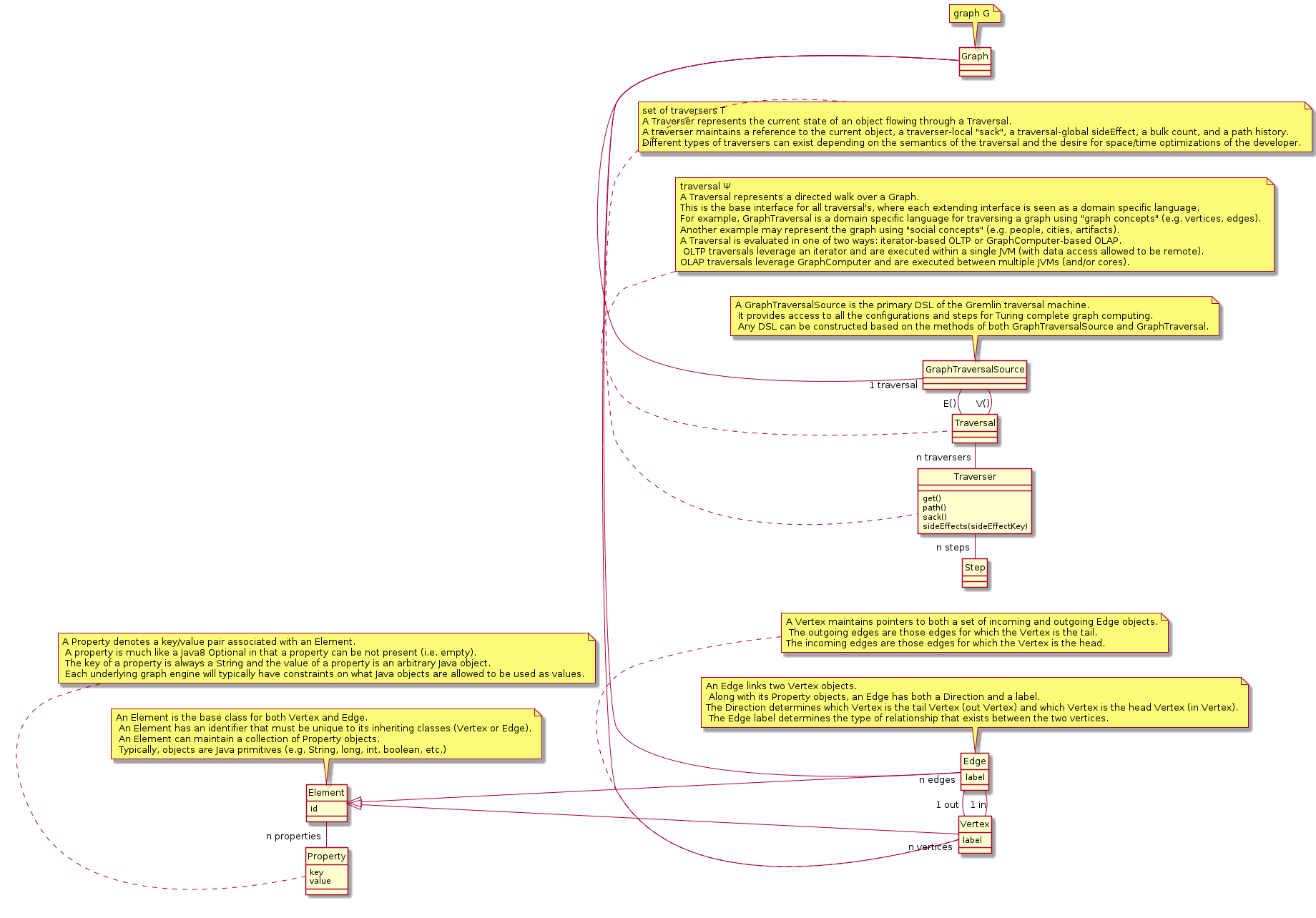
note top of GraphTraversalSource: A GraphTraversalSource is the primary DSL of the Gremlin traversal machine.\n It provides access to all the configurations and steps for Turing complete graph computing.\n Any DSL can be constructed based on the methods of both GraphTraversalSource and GraphTraversal. | note top of GraphTraversalSource: A GraphTraversalSource is the primary DSL of the Gremlin traversal machine.\n It provides access to all the configurations and steps for Turing complete graph computing.\n Any DSL can be constructed based on the methods of both GraphTraversalSource and GraphTraversal. | ||
| − | class GraphTraversalSource [[http://tinkerpop.apache.org/javadocs/current/full/org/apache/tinkerpop/gremlin/process/GraphTraversalSource.html]] { | + | |
| + | class GraphTraversalSource [[http://tinkerpop.apache.org/javadocs/current/full/org/apache/tinkerpop/gremlin/process/traversal/dsl/graph/GraphTraversalSource.html]] { | ||
} | } | ||
note top of Traversal: traversal Ψ\nA Traversal represents a directed walk over a Graph. \nThis is the base interface for all traversal's, where each extending interface is seen as a domain specific language. \nFor example, GraphTraversal is a domain specific language for traversing a graph using "graph concepts" (e.g. vertices, edges). \nAnother example may represent the graph using "social concepts" (e.g. people, cities, artifacts). \nA Traversal is evaluated in one of two ways: iterator-based OLTP or GraphComputer-based OLAP.\n OLTP traversals leverage an iterator and are executed within a single JVM (with data access allowed to be remote). \nOLAP traversals leverage GraphComputer and are executed between multiple JVMs (and/or cores). | note top of Traversal: traversal Ψ\nA Traversal represents a directed walk over a Graph. \nThis is the base interface for all traversal's, where each extending interface is seen as a domain specific language. \nFor example, GraphTraversal is a domain specific language for traversing a graph using "graph concepts" (e.g. vertices, edges). \nAnother example may represent the graph using "social concepts" (e.g. people, cities, artifacts). \nA Traversal is evaluated in one of two ways: iterator-based OLTP or GraphComputer-based OLAP.\n OLTP traversals leverage an iterator and are executed within a single JVM (with data access allowed to be remote). \nOLAP traversals leverage GraphComputer and are executed between multiple JVMs (and/or cores). | ||
Revision as of 23:04, 1 November 2018
Gremlin Paper by Marko Rodriguez
DSL
Concepts
Three interacting components
- a Graph G
- a traversal Ψ
- and a set of Traversers T

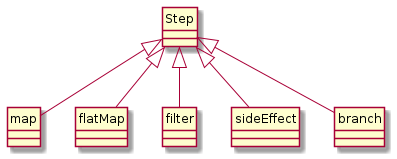
Steps
