SiDIF: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
== SiDIF Structure == | == SiDIF Structure == | ||
=== SiDIF expressions === | |||
A SiDIF expression like | A SiDIF expression like | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
| Line 21: | Line 22: | ||
* City is the object | * City is the object | ||
Such a set of subject / predicate / object is called a {{Link|target=Triple}} | Such a set of subject / predicate / object is called a {{Link|target=Triple}} | ||
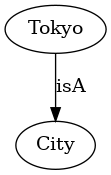
=== graphical representation === | ==== graphical representation ==== | ||
<graphviz> | <graphviz> | ||
digraph cityexample { | digraph cityexample { | ||
Tokyo->City [label="isA"]; | Tokyo->City [label="isA"]; | ||
} | } | ||
</graphviz> | </graphviz> | ||
== SiDIF Implementation == | == SiDIF Implementation == | ||
see https://github.com/BITPlan/org.sidif.triplestore | see https://github.com/BITPlan/org.sidif.triplestore | ||
Revision as of 11:48, 12 March 2015
Introduction
The Simple Data Interchange Format (SiDIF) is yet another format for exchanging data between computers.
SiDIF isA DataInterchangeFormat
is a valid SiDIF content.
Examples
City Tokyo
City isA Concept Tokyo isA City webpage addsTo City "http://www.tokyo.jp" is webpage of Tokyo
SiDIF Structure
SiDIF expressions
A SiDIF expression like
Tokyo isA City
consists of three parts:
- Tokyo is the subject
- isA is the predicate
- City is the object
Such a set of subject / predicate / object is called a Triple
graphical representation
