UML: Difference between revisions
| (9 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
== Stackoverflow Tags == | == Stackoverflow Tags == | ||
# [https://stackoverflow.com/questions/tagged/uml uml] | |||
# [https://stackoverflow.com/questions/tagged/argouml argouml] | # [https://stackoverflow.com/questions/tagged/argouml argouml] | ||
# [https://stackoverflow.com/questions/tagged/magic-draw magicdraw] | # [https://stackoverflow.com/questions/tagged/magic-draw magicdraw] | ||
# [https://stackoverflow.com/questions/tagged/enterprise-architect enterprise architect] | # [https://stackoverflow.com/questions/tagged/enterprise-architect enterprise architect] | ||
# [https://stackoverflow.com/questions/tagged/objectaid objectaid] | |||
# [https://stackoverflow.com/questions/tagged/plantuml plantuml] | |||
# [https://stackoverflow.com/questions/tagged/rational-rose rational rose] | # [https://stackoverflow.com/questions/tagged/rational-rose rational rose] | ||
# [https://stackoverflow.com/questions/tagged/umbrello umbrello] | # [https://stackoverflow.com/questions/tagged/umbrello umbrello] | ||
| Line 13: | Line 16: | ||
# [https://stackoverflow.com/questions/tagged/visual-paradigm visual paradigm] | # [https://stackoverflow.com/questions/tagged/visual-paradigm visual paradigm] | ||
# [https://stackoverflow.com/questions/tagged/staruml staruml] | # [https://stackoverflow.com/questions/tagged/staruml staruml] | ||
== Tool-Evaluations == | == Tool-Evaluations == | ||
* https://www.herzbube.ch/article/evaluation-free-uml-tools | * https://www.herzbube.ch/article/evaluation-free-uml-tools | ||
* https://www.predictiveanalyticstoday.com/open-source-free-unified-modeling-language-uml-tools/ | * https://www.predictiveanalyticstoday.com/open-source-free-unified-modeling-language-uml-tools/ | ||
== Historic Tools == | |||
* [https://web.archive.org/web/20060203054943/http://www.microgold.com/ MicroGOLD withClass] | |||
== Stackoverflow Questions == | == Stackoverflow Questions == | ||
=== Inheritance === | === Inheritance === | ||
| Line 21: | Line 28: | ||
When implementing inheritance there is usually some cost involved in terms of extra classes, tables, documentation and other results that need to be created after the decision to use inheritance. | When implementing inheritance there is usually some cost involved in terms of extra classes, tables, documentation and other results that need to be created after the decision to use inheritance. | ||
Inheritance is about special and general cases. First you might want to ask what is the difference between the cases - (called a | Inheritance is about special and general cases. First you might want to ask what is the difference between the cases - (called a {{Link|target=Discriminator}}). In your case it is the type of reservation and you could avoid the inheritance by modelling this type of reservation and implementing the different behavior based on the reservation type. That would lead to a design like: | ||
==== Avoiding inheritance ==== | |||
<uml> | <uml> | ||
hide circle | hide circle | ||
class Reservation { | class Reservation { | ||
reservationtype:enum{normal,regular} | |||
date: Date | date: Date | ||
duration: int | duration: int | ||
price: int | price: int | ||
delete(): boolean | delete(): boolean | ||
start:date | |||
end:date | |||
frequency:int | |||
new(date,optional date,optional int) | |||
} | } | ||
class Client { | class Client { | ||
name | name | ||
} | } | ||
Reservation -> Client | |||
Reservation "n" <- "1" Reservation | |||
</uml> | </uml> | ||
==== | If the inheritance has a high benefit because there are a lot of extra attributes, relation or operations for each special case then you can apply it. | ||
In this case there is | |||
* an extra 1:n relation between regular reservation and reservation (which was not visible in your design but implied by the attribute regular Reservation) | |||
and there are some extra fields | |||
* start date | |||
* end date | |||
* frequency | |||
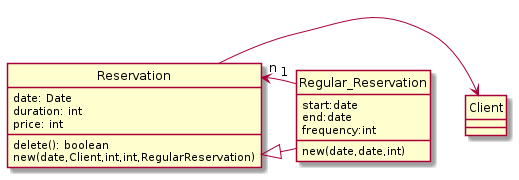
What is missing at this time is common behavior that would make it sensible to apply inheritance. In the image below I added the generalization nevertheless. It would not be needed at this point in time but as soon as there are general operations you would like to apply to any type of reservation: | |||
==== Applying inheritance ==== | |||
<uml> | <uml> | ||
hide circle | hide circle | ||
| Line 42: | Line 72: | ||
price: int | price: int | ||
delete(): boolean | delete(): boolean | ||
new(date,Client,int,int,RegularReservation) | |||
} | |||
class Regular_Reservation { | |||
start:date | start:date | ||
end:date | end:date | ||
frequency:int | frequency:int | ||
new(date, | new(date,date,int) | ||
} | } | ||
Reservation -> Client | Reservation -> Client | ||
Reservation "n" <- "1" | Reservation <|-- Regular_Reservation | ||
Reservation "n" <- "1" Regular_Reservation | |||
</uml> | </uml> | ||
= Learning UML = | = Learning UML = | ||
{{Link|target=UML-Day}} | {{Link|target=UML-Day}} | ||
[[Category:UML]] | |||
Latest revision as of 10:45, 16 February 2023
Tools
Stackoverflow Tags
- uml
- argouml
- magicdraw
- enterprise architect
- objectaid
- plantuml
- rational rose
- umbrello
- umlet
- visual paradigm
- staruml
Tool-Evaluations
- https://www.herzbube.ch/article/evaluation-free-uml-tools
- https://www.predictiveanalyticstoday.com/open-source-free-unified-modeling-language-uml-tools/
Historic Tools
Stackoverflow Questions
Inheritance
When implementing inheritance there is usually some cost involved in terms of extra classes, tables, documentation and other results that need to be created after the decision to use inheritance.
Inheritance is about special and general cases. First you might want to ask what is the difference between the cases - (called a Discriminator). In your case it is the type of reservation and you could avoid the inheritance by modelling this type of reservation and implementing the different behavior based on the reservation type. That would lead to a design like:
Avoiding inheritance
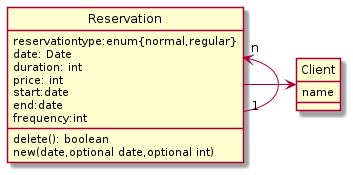
If the inheritance has a high benefit because there are a lot of extra attributes, relation or operations for each special case then you can apply it.
In this case there is
- an extra 1:n relation between regular reservation and reservation (which was not visible in your design but implied by the attribute regular Reservation)
and there are some extra fields
- start date
- end date
- frequency
What is missing at this time is common behavior that would make it sensible to apply inheritance. In the image below I added the generalization nevertheless. It would not be needed at this point in time but as soon as there are general operations you would like to apply to any type of reservation:
Applying inheritance