Pynomina/ledger
Wolfgang Fahl
Ledger Book[edit]
The pynomina Ledger Book model consists of four main classes:
- Book
- Account
- Transaction
- Split
These are the necessary classes which work together to represent a comprehensive financial ledger records.
Class Structure[edit]
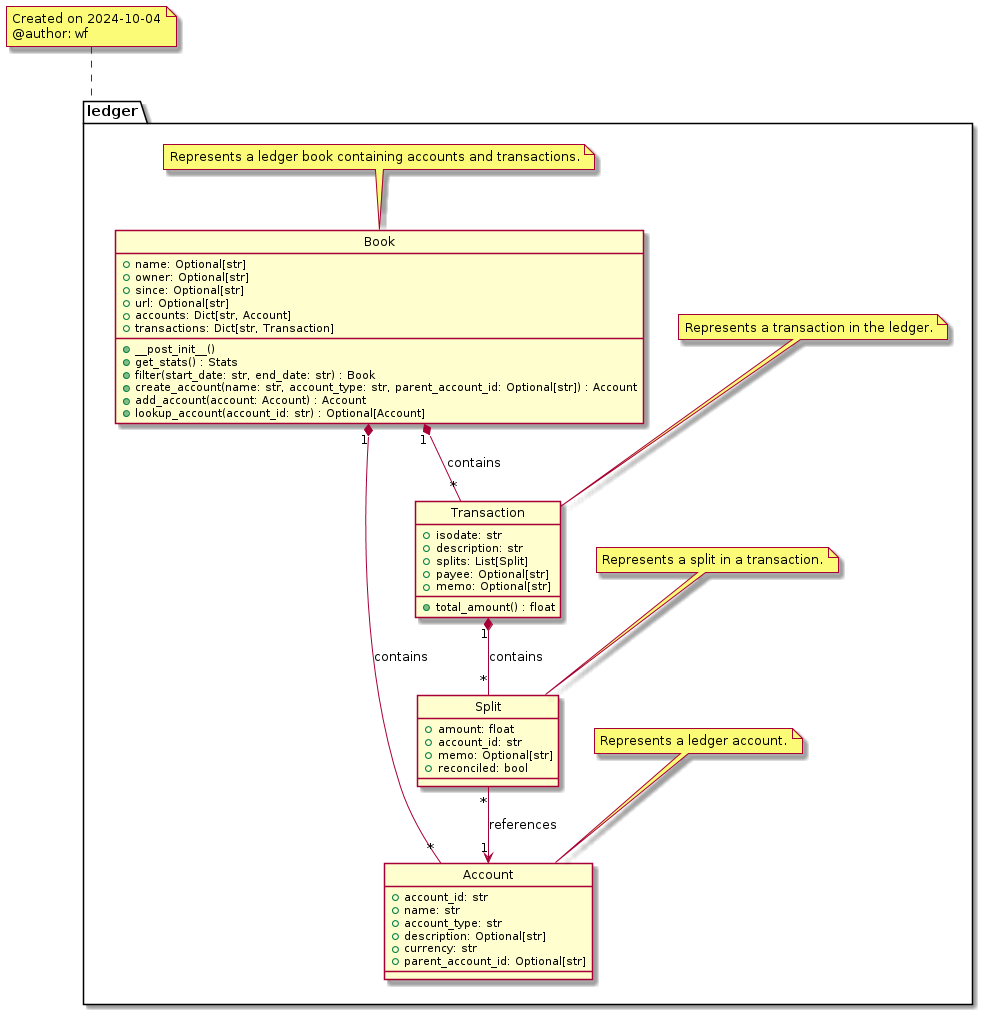
Book[edit]
The Book class represents the main container for all financial data. It includes:
- Basic information: name, owner, creation date, and source URL
- Collections of accounts and transactions
- Methods for managing accounts and transactions, including:
- get_stats(): Retrieves statistics about the book
- filter(): Filters transactions by date range
- create_account(): Creates a new account
- add_account(): Adds an account to the book
- lookup_account(): Finds an account by ID
Account[edit]
The Account class represents a hierarchy of individual financial accounts within the ledger. It includes:
- account_id: Unique identifier for the account
- name: Human-readable account name
- account_type: Type of account (e.g., EXPENSE, INCOME)
- description: Optional account description
- currency: Account currency (default: EUR)
- parent_account_id: Optional parent account for hierarchical structure
Transaction[edit]
The Transaction class represents individual financial transactions. It includes:
- isodate: Date of the transaction in International Standards Organization date format yyyy-mm-dd
- description: Description of the transaction
- splits: List of Split objects representing the movement of money
- payee: Optional payee information
- memo: Optional additional notes
- total_amount(): Method to calculate the total transaction amount
Split[edit]
The Split class represents the individual components of a transaction, showing how money moves between accounts. It includes:
- amount: The amount of money involved in the split
- account_id: The account associated with this part of the transaction
- memo: Optional notes for this split
- reconciled: Boolean indicating if the split has been reconciled
Example Data[edit]
Here's an example of how the ledger model is used in practice:
Yaml Format[edit]
owner: Wolfgang Fahl
url: https://github.com/WolfgangFahl/pynomina/blob/main/nomina_examples/expenses2024.yaml
since: 2024-10-06
accounts:
Expenses:
account_id: Expenses
name: Expenses
account_type: EXPENSE
description: 'General Expenses'
currency: EUR
Expenses:Food:
account_id: Expenses:Food
name: Dining
account_type: EXPENSE
description: 'Expenses for Food'
currency: EUR
parent_account_id: Expenses
Cash in wallet:
account_id: Wallet
name: Cash in Wallet
account_type: EXPENSE
description: ''
currency: EUR
transactions:
Bakery2024-10-06_0900_1:
isodate: '2024-10-06'
description: Bread
splits:
- amount: -3.50
account_id: Cash in Wallet
- amount: 3.50
account_id: Expenses:Dining
memo: Fresh sourdough bread
Bakery2024-10-06_0900_2:
isodate: '2024-10-06'
description: Buns for Breakfast
splits:
- amount: -2.40
account_id: Cash in Wallet
- amount: 2.40
account_id: Expenses:Dining
memo: 4 whole grain buns
Implementation[edit]
The ledger model is implemented in Python, utilizing dataclasses and type hinting for clear and maintainable code. The `@lod_storable` decorator is used to enable easy serialization and deserialization of the data in YAML and/or JSON and other formats. The core idea is that the records should be readily available an tabular "list of dicts (lod)" format.