Difference between revisions of "SoftReferences for Traceability"
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
} | } | ||
</graphviz> | </graphviz> | ||
| − | + | ||
The traditional view of TDD seems to be something like | The traditional view of TDD seems to be something like | ||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
There are many cases for this. Very common is that the clarification of requirements is initiated by feedback from the software as it is realized. Also people might change their mind or come of with new ideas. This interaction cycle is a very strong reason to work incrementally and interatively and has been a big motivitation for the agile movement. | There are many cases for this. Very common is that the clarification of requirements is initiated by feedback from the software as it is realized. Also people might change their mind or come of with new ideas. This interaction cycle is a very strong reason to work incrementally and interatively and has been a big motivitation for the agile movement. | ||
| + | }} | ||
[[Category:frontend]] | [[Category:frontend]] | ||
Revision as of 11:16, 18 October 2018
| BlogEntry | |
|---|---|
| date | 2018/10/18 |
| title | SoftReferences for Traceability |
| author | Wolfgang Fahl |
SoftReferences for Traceability
This morning I was developing a JUnit Testcase for a current project. I found it very rewarding and useful to do this work. One step in the process was to apply "design for testability". I had to test a piece of code that was some 30 lines long and part of another function that was already some 60 lines long. In the process the 30 lines became another independent function. This has the effect to make it testable independently and also cleaning up the code since now both functions where only half a page long which makes the code much more readable. Also things get reusable this way. I could keep going on an arguing in favor of test driven development and design for testability. What struck me this morning was that I remembered a presentation "TDD where did all go wrong" in which Ian Cooper told the story of TDD projects that were not going well (enough) and why in recent projects he has seen a lot less TDD.
One of the arguments was that test code was extra code and needed modification far too often even if the requirements had not changed or only slightly changed. It seems to me that this dicussion leads to the question of the value of the three items
- requirement
- code
- testcode
Quite a bit of the arguments in software engineering seem to revolve around the question "What is more valuable?". Some will answer that code is the only result you need and keeping track of the requirements and writing test code is just Muda or "enterprisy cruft".
You'll find a lot of other positions e.g. the one that I am going to take to today that are based on the traceability triangle of the three items shown as a graph below:
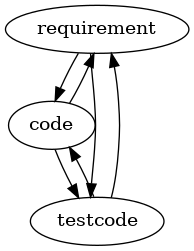
The traditional view of TDD seems to be something like
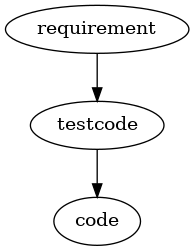
with the assumption that software development is working like a "pipeline" where you give your requirements as inputs and then work from there. Even in agle projects that are based e.g. on user stories the initial input comes from the users's requirements. From the second requirement on you might see the effect that there is a need for refactoring. An additional requirement or a modification of a requirements leads to a change of your code and may be of the testcode.
So this explains some of the links in the graph above. What some people find strange is that coding might lead to changing requirements and also writing testcode. Why should coders and testers have an influence on the needs of the people that asked for the software originally?
There are many cases for this. Very common is that the clarification of requirements is initiated by feedback from the software as it is realized. Also people might change their mind or come of with new ideas. This interaction cycle is a very strong reason to work incrementally and interatively and has been a big motivitation for the agile movement. }}